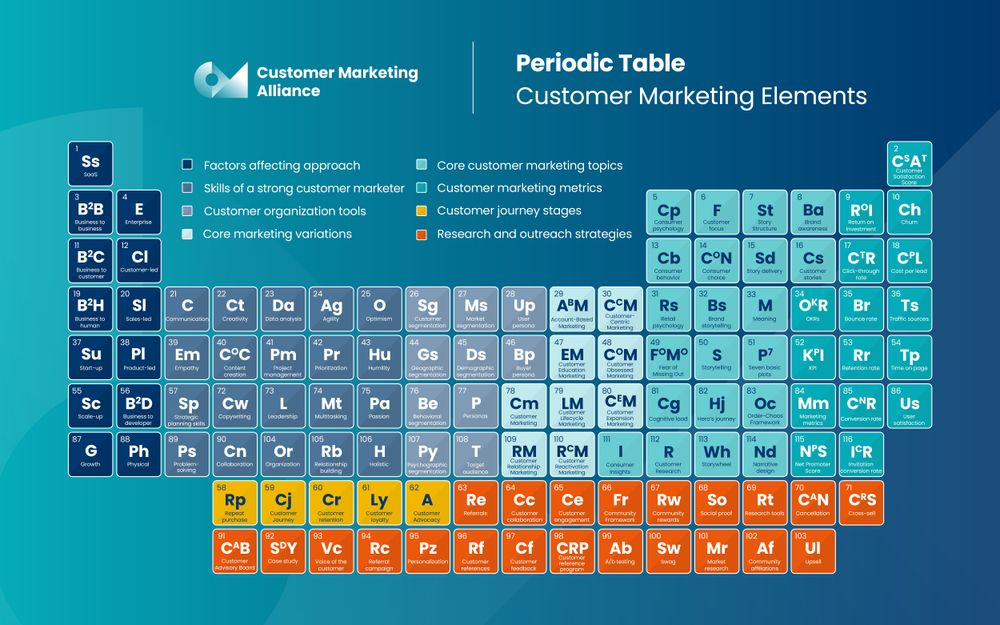
Customer marketing is a science. Along with needing to do research, conduct experiments, and prove findings, customer marketing also has its fair share of specific concepts and lingo you'll have to learn.
Here you'll find Customer Marking Alliance's comprehensive and close-to-complete customer marketing glossary table. While the dictionary of customer marketing lingo will always be expanding as the role evolves, here's what we have so far:
Factors affecting approach:
Ss - SaaS
SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a business that offers software as their product, and is usually provided on a subscription basis. Some SaaS customer marketers may use, are platforms that enable them to streamline and automate various marketing processes, such as email marketing, customer relationship management (CRM), analytics, and more.
Ph - Physical
This refers to businesses that produce physical products
B2B - Business to business
(B2B) Businesses that cater toward other businesses.

B2C - Business to customer
(B2C) Businesses that cater toward individual customers rather than organizations.
B2H - Business to human
(B2H) This is a concept that is consciously chosen by companies to emphasize the importance of catering to the individual rather than a customer segment or organization.
Su - Start-up
A start-up is a company in the early stages of development, often driven by a small team or individual entrepreneur.
Sc - Scale-up
Once a business has successful passed the start-up faze, they are now in a stage of significant growth in terms of revenue, customer base, and market presence. This is scale-up.
G - Growth
Growth is when a business is experiencing an increase in customer acquisition, retention, and revenue for a business.

E - Enterprise
Enterprise refers to a large-scale organization known for their complex structures, resources, and capabilities.
Cl - Customer-led
Customer-led is a an approach where the needs, preferences, and feedback of customers play a central role in shaping your businesses strategies and initiatives.
Sl - Sales-led
Sales-led businesses have the primary focus on generating revenue and driving sales.
Pl - Product-led
A product-led approach focuses on providing the best product experience. Your product or service will take a central role in driving customer acquisition, engagement, and retention.
B2D - Business to developer
(B2D) Businesses that specifically cater toward developers.
Skills of a strong customer marketer:
C - Communication
Communication can refer to the ease and ability to form and maintain a dialogue both internally and externally. Effective communication in customer marketing specifically wants to fostering positive relationships to support growth through retention and advocacy.
Em - Empathy
Empathy is one of the most important skills for a customer marketer to form meaningful connection with customers, so it's crucial to understand their needs and motivations.
Sp - Strategic planning skills
Strategic planning is crucial for leveraging customer collaboration and solving problems. This is a skill that uses past experiences to inform new strategies.
Ps - Problem-solving
This skill involves effectively addressing position-specific challenges and learning from them for future solutions.
Ct - Creativity
Customer marketers must have creativity in order to generate innovative ideas, concepts, and strategies that engage and resonate with customers.
COC - Content creation
Customer marketers produce and develop valuable, relevant, and engaging content to attract, inform, and engage the target audience.
Cw - Copywriting
Copywriting in customer marketing is the art and skill of crafting persuasive and compelling written content that resonates with the target audience.
Cn - Collaboration
Collaboration for customer marketing is the act of partnering and working closely with internal teams, stakeholders, and even customers to create content, campaigns, and initiatives.
Da - Data analysis
Data analysis involves examining and interpreting customer-related data to gain insights and make informed marketing decisions.
Pm - Project management
Project management is the practice of planning, organizing, and executing marketing initiatives to achieve specific goals
L - Leadership
Customer marketers should have the skill of creating a leadership style that guides, inspires and influences the team towards achieving marketing objectives.. It involves setting a clear vision, providing strategic direction, and empowering team members to excel in their roles.

Or - Organization
Organization is how you structure your marketing activities, resources, and processes to achieve desired outcomes.
Ag - Agility
Agility in marketing is your company's ability to quickly and effectively adapt to changing market conditions, consumer behaviors, and emerging trends.
Pr - Prioritization
ranking the order of marketing tasks, initiatives, and objectives by importance and urgency.
Mt - Multitasking
The ability to work on multiple objectives at once without having to compromise. Its a careful balancing of resources and efforts to acheive effective ROI for all projects.
Rb - Relationship building
This is one of the most important skills for a customer marketer. Bruilding relationships will help foster customer loyalty, retention, and increase overall customer lifetime value. It involves nurturing these relationships based on trust, communication, and mutual value.
O - Optimism
Maintaining a hopeful and confident attitude despite challenges and setbacks is a valuable trait of a customer marketer. Such an outlook will fuel creativity, resilience, and the ability to see potential opportunities.
Hu - Humility
Humility is the quality of approaching marketing with a modest and open mindset, recognizing that there is always more to learn and discover.
Pa - Passion
Passion for customer marketers involves a deep connection and commitment to understanding and meeting customer needs and desires.
H - Holistic
A holistic approach to customer marketing involves taking in a 360-degree view of the customer, considering their needs, preferences, and interactions across various touchpoints with the aim to create a seamless and consistent customer experience.
Customer organization tools:
Sg - Customer segmentation
This involves dividing the customer base into distinct segments to better understand their unique needs, motivations, and purchase patterns based on shared characteristics, behaviors, and preferences.

Gs - Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides your target market based on different geographical areas. It helps you tailor you strategies and offers to better suit the specific needs and preferences of people in each location.
Be - Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral segmentation categorizes your customer base depending on their observable behaviors and actions. It involves analyzing things like purchase history, product usage, website interactions, and response to marketing campaigns.
Py - Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation is when businesses categorize their target market based on shared personality traits, values, interests, attitudes, and lifestyles. It helps them understand what makes people tick and craft marketing messages that resonate with their unique mindset and preferences.
Ms - Market segmentation
Market segmentation slices up your market based on things like age, location, or interests. Think of it as breaking down a big crowd into smaller squads for a more personalized approach. Market segmentation can include things like geographic, psychographic, and behvaioral segmentation within it.
Ds - Demographic segmentation
This segmentation is based on characteristics like age, gender, income, and education. This'll ensure your products and messages are reaching the right crowd.
P - Personas
Personas are fictional characters that represent different types of customers. They can be used to represent different segments of your audience. Giving these groups names, personalities, and needs, means you can start to imagine who you're selling to make strategies that connect with real people. Remember that personas will not work at the individual level.
T - Target audience
The target audience is the specific group of people that your team aims to reach with its strategies and messaging. It's like the bullseye of your marketing efforts.
Up - User persona
User personas are a more specific part of personas. These are personas created with only your product users in mind. By fleshing out these personas you can make better decisions for your existing customers.
Bp - Buyer persona
Buyer personas fictional representation of an ideal customer. This'll encompass key characteristics, behaviors, motivations, and preferences of a target audience segment. Unlike user personas, buyer personas cover both existing and potential customers.
Core marketing variations:
Cm - Customer Marketing
Customer marketing is marketing for existing customers to nurture and retain them. It's like giving a little extra love and attention to the folks who already believe in your brand. Personalized experiences, upselling, and relationships produced by customer marketers, will keep your customers coming back for more.
RM - Customer Relationship Marketing
This is all about building and maintaining strong connections with customers for the long haul. It's like being best buds with your customers and showing them that they're valued by your business. Doing so will improve retention, engagement, and the longevity of your customers.
ABM - Account-Based Marketing
Account-based marketing focuses on targeting specific accounts or companies, rather than a broad audience. It'll prioritize personalized marketing campaigns and messaging that are tailored to the unique needs and interests of each account.
EM - Customer Education Marketing
This is a strategic approach equips customers with the knowledge and skills they need to get the most out of your product or service. Create educational content, resources, and experiences to empower customers and support their success.
LM - Customer Lifecycle Marketing
This strategy is built to nurture relationships with customers at every stage of the customer journey, from initial discovery to post-purchase loyalty and advocacy. These practices will increase the longevity of the relationship too, improving customer value too.

RCM - Customer Reactivation Marketing
Rekindling relationships with dormant or inactive customers is an important component to stabalizing customer growth. Entice them with irresistible offers and personalized messages to reignite their interest and loyalty.
CCM - Customer-Centric Marketing
This means putting customers at the heart of everything you do. From how you evolve your products, messaging, and marketing techniques to ensure you business growth alongside your customers.
COM - Customer Obsessed Marketing
Customer obsession is customer-centricity to the extreme. This means going above and beyond your customer's expectations with every interaction to ensure retention, loyalty, and advocacy.
CEM - Customer Expansion Marketing
This marketing aims to maximise the value of your existing customers using upselling and cross-selling by offering them additional products and upgrades that align with their needs and desires.
Core customer marketing topics:
I - Consumer Insights
Consumer insights help you understand what makes your target audience tick. These nuggets of wisdom are gained through research, surveys, and data analysis, and serve as the guiding marks to create products, messaging, and experiences that connect with your audience on a deeper level.
Cp - Consumer psychology
Consumer psychology is the science that figure out the "why" behind consumer's buying decisions. It studies how people's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that impact their purchase decisions. These insights can help you tailor your marketing to influence these choises.
Cb - Consumer behavior
Like consumer psychology, consumer behavior studies customers actions, but specifically how they select, purchase, use, and dispose of products and services.
Rs - Retail psychology
This is like the secret playbook that retailers use to manipulate store layouts, product placements, and even scents to influence consumer buying decisions and create a more enticing shopping experience.
FOMO - Fear of missing out
FOMO, or Fear of Missing Out, is that nagging feeling that urges us to join the party, buy the product, or be part of the trend, for fear of being left out. It's one of the reasons customers make impulse purchases.
Cg - Cognitive load
Cognitive load refers to the mental load required by your customers to process and comprehend your marketing messages or content. Minimizing cognitive load means simplifying and optimizing how you present the information used in your marketing to make it easier for customers to understand, remember, and make decisions.
R - Customer Research
The umbrella term for the process that gathering information about customers through surveys, interviews, and data analysis. This'll include segmentation, consumer psychology, and more.

F - Customer focus
It's the mindset of prioritizing and catering to the needs, wants, and satisfaction of your customers above all else.
CON - Consumer choice
The consumers ability to make decisions based on personal preferences, tastes, and needs.
Bs - Brand storytelling
Brand storytelling uses a brand's values, purpose, and identity to produce narratives that captivate your target audience. It involves crafting compelling stories that connect on an emotional level, fostering brand loyalty and deeper connections.
S - Storytelling
Storytelling is a narrative, usually one in which a change happens, either concluding in a positive or negative end. Through these narratives, you can explore ideas, beliefs, experiences, and certain events.
Hj - Hero’s journey
It's a story pattern where the hero faces a call to action, encounters obstacles, discovers inner strength, and ultimately returns transformed; From Frodo's quest of destroy the ring to Luke Skywalker's battle against the dark side.

Wh - Storywheel
The storywheel is like a storytelling roadmap that breaks down the elements of a story, from setting the stage to introducing characters, building tension, and resolving conflicts. It's a visual representation you can use to get an overview of your story and its possibilities.
St - Story Structure
The blueprint that outlines the beginning, middle, and end of a story, organizing key elements like plot, characters, and conflicts.
Sd - Story delivery
This is how you present and share your story, whether through spoken word, written text, visuals, or multimedia.
M - Meaning
It's the people, experiences, or things that resonates with you. Whether it's finding meaning in relationships, work, or personal pursuits, it's that intangible ingredient that provides a sense of fulfillment to your journey.
P7 - Seven basic plots
Christopher Booker argues that you can boil every single story down to one of seven basic plots: Overcoming the monster, rags to riches, the quest, voyage and return, comedy, tragedy, and rebirth.
Oc - Order Chaos Framework
It's a storytelling approach where a structured order is established, only to be disrupted by chaos or conflict, leading to transformation and resolution.
Nd - Narrative design
This is the act of crafting of narratives to convey a desired message or experience.
Ba - Brand awareness
Brand awareness refers to the level of recognition and familiarity that consumers have with your brand. It measures the extent to which a brand name, logo, or product is known and remembered by the target audience.
Cs - Customer stories
Customer stories are firsthand accounts about customer experiences with a product, service, or brand. They serve as testimonials that help build trust, credibility, and connections with prospective customers.
Customer marketing metrics:
OKR - OKRs
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) is a goal-setting framework used to define and measure progress towards achieving desired outcomes. Specifically, they are ambitious and qualitative statements that represent your team's aims.
KPI - KPI
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics used to evaluate your performance and progress over a given time. They serve as measurable benchmarks that reflect the success or effectiveness of a particular activity, process, or goal.
Mm - Marketing metrics
Marketing metrics enable marketers to track progress, evaluate success, and make informed decisions to optimize strategies and drive business growth. This can include conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI), retention and churn rates, and more.

NPS - Net Promoter Score
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a customer loyalty metric that measures how willing customers are to recommend a product, service, or brand to others. It asks customers to rate their likelihood of recommending on a scale of 0-10.
ROI - Return on Investment
Return on Investment (ROI) is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability and efficiency of an investment. ROI provides insights into the effectiveness of an investment, helping organizations make informed decisions and allocate resources wisely to maximize returns.
CTR - Click-through rate
CTR or click-through rate measures the percentage of people who click on a specific link or call-to-action within a marketing campaign or advertisement. It indicates the level of engagement and effectiveness of the marketing message used.
Br - Bounce rate
Bounce rate refers to the percentage of website visitors who leave a site without engaging with it, or navigating to other pages. A high bounce rate generally indicates that visitors are not finding your website or content engaging enough to stay on the site.
Rr - Retention rate
Retention rate is the percentage of customers or users who continue to engage or stay with a product, service, or organization over a certain period of time.
CNR - Conversion rate
Conversion rate is the percentage of people who take a desired action, like making a purchase or filling out a form, out of the total number of visitors to a website or users of a product. It helps measure how effectively a company can turn potential customers into actual buyers or subscribers.
ICR - Invitation conversion rate
This is the percentage of people who accept an invitation or request to join a specific event, program, or community, out of the total number of invitations sent. It measures the effectiveness of the invitations in convincing people to participate or join.
CSAT - Customer Satisfaction Score
CSAT is a metric used to measure how satisfied customers are with a product, service, or interaction with a company. CSAT helps companies understand how well they are meeting customer expectations.
Ch - Churn
Churn is the rate at which customers discontinue or cancel their connection to your company.
CPL - Cost per lead
Cost per lead (CPL) is a metric used in marketing to calculate the average cost of acquiring a potential customer's contact information or generating a lead. It represents the amount of money spent on marketing and advertising efforts divided by the number of leads obtained.
Ts - Traffic sources
These are the channels or platforms through which visitors or users arrive at a website or online platform. They can include search engines, social media platforms, email marketing campaigns, direct visits, or referrals from other websites.
Tp - Time on page
This refers to the time a visitor spends on a particular web page before navigating to another page or leaving the website altogether. It is a metric used to measure user engagement and the level of interest in the content.
Us - User satisfaction
This measures how well your offers meet or exceed user expectations, addresses their needs, and provides a positive user experience.
Customer journey stages:
Rp - Repeat purchase
Repeat purchase refers to the act of a customer making a subsequent purchase of a product or service from the same company or brand. Repeat purchases are important for businesses as they contribute to customer loyalty, revenue growth, and long-term success.
Ly - Customer loyalty
Customer loyalty refers to the tendency of customers to consistently choose a particular brand or company over its competitors. It reflects the degree of attachment, trust, and preference that customers have towards a specific business.
Cj - Customer Journey
This is the entire path or sequence of interactions and experiences that a customer goes through when engaging with a company or brand.
A - Customer Advocacy
This is when satisfied customers become advocates for your brand by sharing positive experiences, providing testimonials, or referring new customers. It's valuable for businesses as it leads to word-of-mouth marketing, increased credibility, and the potential for acquiring new customers through trusted recommendations.
Cr - Customer retention
This refers to the ability of a business to maintain and keep existing customers over a certain period of time. It involves strategies and efforts aimed at ensuring customers continue to engage with and make repeat purchases from the company.
Research and outreach strategies:
Vc - Voice of the customer
VOC involves gathering and analyzing customer insights through surveys, reviews, feedback forms, and other channels to understand their needs, expectations, and satisfaction levels.

CAB - Customer Advisory Board
A customer advisory board is a group of selected customers who provide insights, feedback, and guidance to a company regarding its products, services, or strategies. They serve as a representative voice of the customer, offering valuable perspectives and recommendations.

Rc - Referral campaign
A referral campaign is a marketing initiative that encourages existing customers to refer new customers to a company or brand. It typically involves offering incentives or rewards to customers for successfully referring others.
SDY - Case study
A case study refers to a examination of a customer's experience with one of your products or services. They're valuable tools to highlight success stories, build credibility, and inspire potential customers by demonstrating real-life examples of the benefits and value a product or service can provide.
Pz - Personalization
This involves tailoring and customizing experiences, content, or offerings to meet the specific needs and preferences of individual customers.
Re - Referrals
This is an act of recommending or suggesting a product, service, or brand to others based on positive experiences. It involves customers sharing their satisfaction with others and encouraging them to try or purchase the offering.
Rf - Customer references
Customer references are individuals or companies who have used a product or service and are willing to vouch for its quality, benefits, and positive outcomes. They serve as testimonials or examples of successful experiences with a particular offering. Customer references are commonly used by businesses to showcase their credibility, build trust, and influence potential customers in their decision-making process.

Cc - Customer collaboration
This is the process of any strategy actively involving customers in the development, improvement, or decision-making of products, services, or strategies. It involves seeking input, feedback, and ideas from customers to co-create or shape business initiatives.
Cf - Customer feedback
This refers to gathering insights and perspectives directly from customers to understand their satisfaction levels, identify areas for improvement, and make informed business decisions. Customer feedback helps companies enhance their offerings, address issues, and deliver better customer experiences based on the input received from their customers.
Ce - Customer engagement
This refers to the level of interaction, involvement, and emotional connection that customers have with a brand, product, or service. It involves capturing and maintaining the attention and interest of customers through various channels and touchpoints.
CRP - Customer reference program
Customer reference program is a structured initiative by a company to leverage satisfied customers as advocates and sources of positive testimonials. It involves identifying and recruiting customers who are willing to share their experiences and endorse the company's products or services.
Fr - Community Framework
Community framework is a structured approach or model for developing and managing an online community. It involves defining the guidelines, rules, and structure that govern the community's interactions and activities.
Ab - A/b testing
A/B testing compares two versions of a webpage, app, or other digital asset to see which performs better. Users are presented with two variations of the same asset at random, and the one that leads to higher engagement, conversions, or click-throughs will inform the messaging that your target audience responds to.
Rw - Community rewards
Community rewards are incentives or benefits offered to members of an online community for their active participation, contributions, or engagement. They can include perks such as exclusive content, access to special events, discounts, or recognition within the community.
Sw - Swag
This is the name for promotional merchandise or goodies your company or gives away as a form of branding or marketing. It often includes items like t-shirts, hats, pens, stickers, or other promotional materials with a memorable logo or message.
So - Social proof
This is a psychological phenomenon where people look to the actions and behaviors of others to determine what is correct, popular, or trustworthy. When individuals see others engaging with a product, service, or brand positively, they are more likely to perceive it as valuable and reliable.
Mr - Market research
Market research involves gathering and analyzing information about a specific market, industry, or target audience. This can include things like customer research within it.

Rt - Research tools
Research tools are resources, software, or techniques used to collect, analyze, and interpret data for research purposes.
Af - Community affiliations
These are relationships your company will have with certain individual people who will be involved in, and support members of your community based on shared interests, values, or goals.
CAN - Cancellation
Cancellation is the act of terminating or discontinuing a service, subscription, reservation, or agreement.
Ul - Upsell
This is a sales technique of offering customers a higher-priced or upgraded product or service in addition to their original purchase; these will be ones that compliment and support the use case of the individual.

CRS - Cross-sell
This is the strategy of recommending or offering customers related or complementary products or services to go along with their original purchase. This is usually a horizontal expansion, rather than the upgrades usually suggested in upselling.
Know any we missed?
Can you think of any concepts you think we've missed in this list? If so, why no join Customer Marketing Alliance's Slack channel to let us know. And while you're at it, why not start a conversation with the hundreds of customer marketing professionals in our community?






